Fintech
DLP Resources Intersects 214m of 0.43% CuEq* (0.35% Cu, 113.88ppm Mo and 3.95g/t Ag) on the Aurora Project in Southern Peru
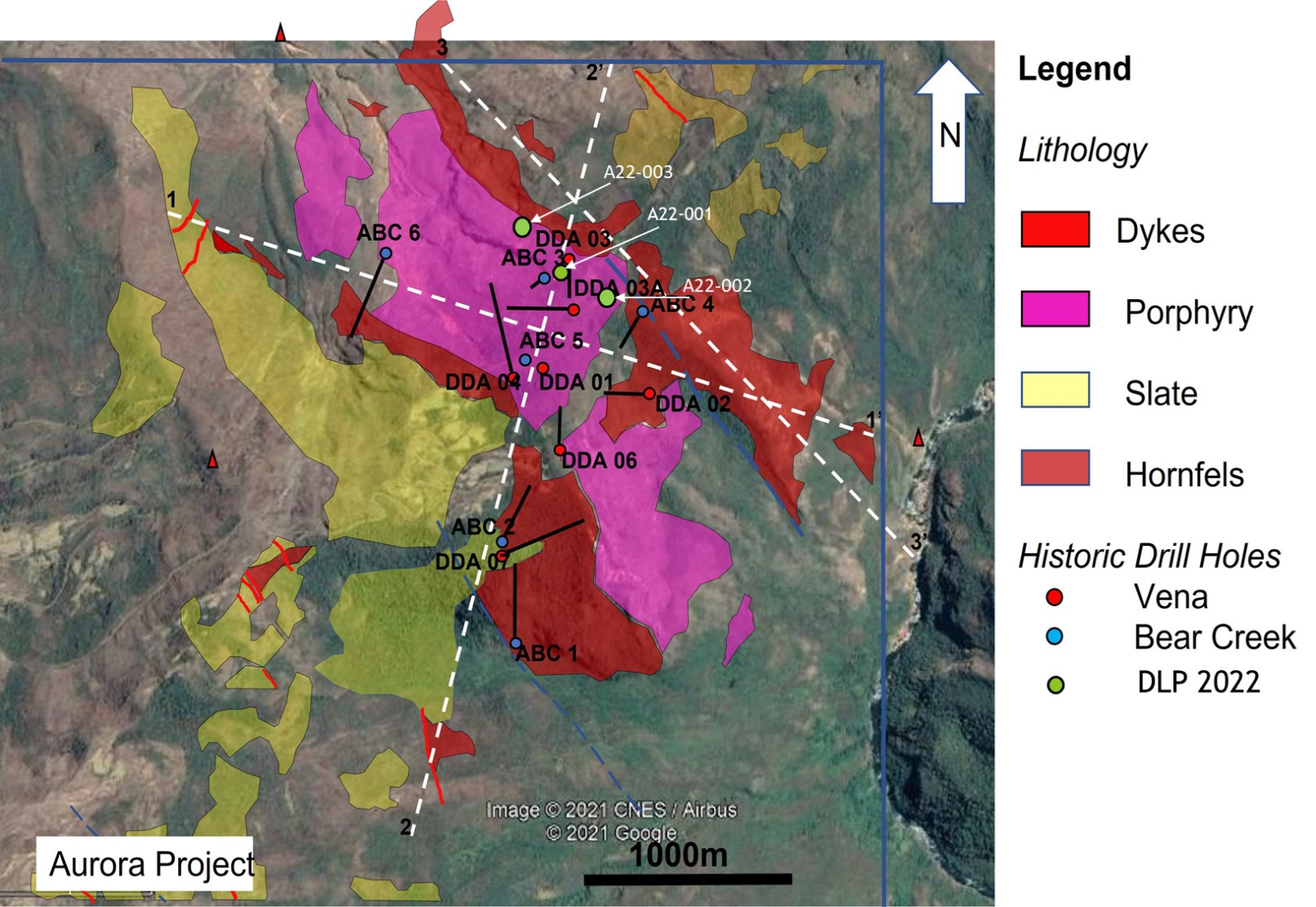
Cranbrook, British Columbia–(Newsfile Corp. – December 5, 2022) – DLP Resources Inc. (TSXV: DLP) (OTCQB: DLPRF) (“DLP” or the “Company“) announces receipt of complete drill results for the first two holes, A22-001 and A22-002 on the Aurora porphyry copper-molybdenum project in southern Peru (Figure 1). In addition, hole A22-003 was completed to a depth of 702.30m on November 30.
Results for the initial 179.2m of Hole A22-001 were released on September 29, 2022 (see DLP Resources Inc. news release of September 29, 2022).
Highlights
In addition to the 123.35m (22.45m to 145.80m) of 0.54% CuEq* (0.49% Cu, 36.49ppm Mo and 4.20ppm Ag) intersected in A22-001 an additional 215.10m of 0.33% CuEq* (0.24% Cu, 167.96ppm Mo and 3.47g/t Ag), was intersected from 179.2m to 388m. The complete set of results for A22-001 are summarized in Table 1 below.
Hole A22-002 returned 214.40m (209m to 422.4m) with 0.43% CuEq* (0.35% Cu, 113.88ppm Mo and 3.95g/t Ag). Within this interval a higher-grade intersection of 52m (244m to 296m) returned 0.61% CuEq* (0.52% Cu, 130.55ppm Mo and 4.53g/t Ag). The complete set of results for A22-002 are summarized in Table 3 below.
Results from these first two holes on the Aurora project have confirmed this is a copper-molybdenum rich porphyry system with copper equivalent grades between 0.33% and 0.91% Cu (Table 1).
Hole A22-003 ended at 702.30m with visually encouraging copper and molybdenum mineralization observed throughout the hole. Samples are in the laboratory for assaying and results are expected at the end of December. Secondary enrichment of copper (chalcocite and covellite) is logged from 112m to 271m with molybdenite-rich veins throughout the lower 300m in quartz feldspar porphyry (see Figure 5).
Mr. Gendall President and CEO commented: “With geological information and results received for two of the three holes drilled to date we are extremely encouraged with the continued definition of the Aurora porphyry copper-molybdenum-silver system. This is a multiphase porphyry with higher grade copper mineralization observed in some narrow, earlier porphyry dykes at higher elevations. We will continue to target the higher-grade porphyry phases at depth”.
Aurora Cu-Mo Project – Summary of Drill Results for A22-001 and A22-002
A22-001
Hole A22-001 was drilled to the NE of the mapped porphyry and hornfels contact at an angle of 70 degrees towards an azimuth of 170 degrees (Table 2, Figures 2, 3 and 4). The logged geology is summarized as follows:
- Partially leached polymictic breccia from 0.50m to 22.45m.
- Mixed limonitic zone of partially leached sulphides consisting mainly of chalcopyrite and pyrite with copper oxides and secondary covellite and chalcocite on fractures in a polymictic breccia with occasional quartz-eye-feldspar porphyry down to 61.60m.
- Mixed limonitic zone of partially leached sulphides (chalcopyrite and pyrite) in silicified siltstone, hornfels and brecciated hornfels with secondary covellite and chalcocite on sulphides and fractures down to 124.30m. Narrow 1-4m thick porphyry rock units cross-cut hornfels.
- Quartz-eye-feldspar porphyry from 124.30m to 135.33m with limonite after chalcopyrite and pyrite and chalcocite and native copper at base of oxidation zone around 128.80m.
- Silicified siltstone and hornfels with occasional porphyry intervals from 128.80m down to 172.90m with chalcopyrite and pyrite and secondary copper sulphides along fractures. A fault zone extends from approximately 145.80m to 172.90m.
- Quartz-sericite altered hornfels, intrusive breccias and quartz-eye feldspar porphyry dykes of 4-7m wide in the upper 27m of the interval from 172.90m to 388.00m. Mineralization included disseminated chalcopyrite, molybdenite, pyrite and pyrrhotite.
Table 1. Summary of Initial Drill Results for Diamond Drill Hole A22-001. All grades are length-weighted averages of samples within the interval reported.
| Hole | From | To | Interval1 | Description | Cu (total) | Mo | Ag | Cueq* |
| ID | m | m | m | % | ppm | ppm | % | |
| A22-001 | 0.50 | 22.45 | 21.95 | Partially Leached | 0.12 | 51.23 | 2.98 | 0.17 |
| 22.45 | 388.00 | 365.55 | Oxidized/Mixed/Primary | 0.33 | 114.16 | 3.64 | 0.41 | |
| Includes | 22.45 | 145.80 | 123.35 | Oxidized/Mixed | 0.49 | 36.49 | 4.20 | 0.54 |
| Includes | 100.35 | 145.80 | 45.45 | Enriched | 0.64 | 17.41 | 3.40 | 0.68 |
| Includes | 100.35 | 124.30 | 23.95 | Enriched | 0.87 | 23.70 | 3.43 | 0.91 |
| Includes | 108.65 | 124.30 | 15.65 | Enriched | 1.09 | 32.75 | 3.00 | 1.10 |
| 145.80 | 172.90 | 21.10 | #Fault zone/Mixed | 0.23 | 68.79 | 1.16 | 0.27 | |
| 172.90 | 388.00 | 215.10 | Primary | 0.24 | 167.96 | 3.47 | 0.33 | |
| Includes | 298.85 | 326.00 | 27.15 | Primary | 0.48 | 31.15 | 7.01 | 0.56 |
| Includes | 366.00 | 388.00 | 22.00 | Primary – Mo rich | 0.21 | 573.45 | 1.43 | 0.42 |
Note: *Copper equivalent grades (CuEq) are for comparative purposes only. Calculations are uncut and recovery is assumed to be 100% for the first 145.80m and from 172.90m to 388m as the project is at an early stage of exploration and there is insufficient metallurgical data for estimation of metal recoveries.
# From 145.80m to 172.90m core recovery is estimated to be 78% of interval due to the fault zone and is “incomplete” and “not representative” of metal grades reported. Cueq value for this interval is “not representative”.
*Copper-equivalence is calculated as: CuEq (%) = Cu (%) + [3.55 × Mo (%)] + [0.0095 × Ag (g/t)], utilizing metal prices of Cu – US$3.34/lb, Mo – US$11.86/lb and Ag – US$21.87/oz.
1 Intervals are downhole drilled core lengths. Drilling data to date is insufficient to determine true width of mineralization. Assay values are uncut.
Table 2: A22-001 Diamond drill hole location, depth, orientation and dip.
| Hole | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Length | Azimuth | Dip |
| ID | m | m | Degrees | Degrees | ||
| A22-001 | 190,082 | 8,566,230 | 2801 | 388 | 170 | 70 |
Co-ordinates are in WGS84 Zone 19S
A22-002
Hole A22-002 was drilled to the NE of the mapped porphyry and hornfels contact at an angle of 60 degrees towards an azimuth of 235 degrees (Table 4, Figures 2, 3 and 4). The logged geology is summarized as follows:
- Leached hornfels, intermineral porphyry dyke and intrusive breccia from 0.10m to 89.40m. Quartz-sericite with intermediate argillic alteration predominates with limonite throughout. Limonite occurs throughout with trace sulphides of pyrite and chalcopyrite.
- Partially leached zone within hornfels and intrusive breccias occur from 89.40m to 208.00m Mixed limonitic zone of partially leached sulphides consisting mainly of chalcopyrite and pyrite with secondary covellite and chalcocite on fractures in intrusive breccia. Molybdenite veinlets up to 2cm in width are scattered throughout. Sericite and intermediate argillic alteration predominate with limonite.
- From 208.00m to 422.40 is a mixed zone of partially leached sulphides (chalcopyrite and pyrite) in quartz-sericite and intermediate argillic altered hornfels, intrusive breccias and quartz-eye feldspar porphyries with secondary covellite and chalcocite on sulphides and fractures from 208.00m to 251.3. Enriched copper zone.
- Quartz-sericite with overprint of intermediate argillic alteration of hornfels, intrusive breccias and quartz-eye feldspar porphyry dykes of 4-20m wide occur throughout this interval from 251.3m to 422.40m. Mineralization included disseminated chalcopyrite, molybdenite, pyrite and pyrrhotite. Quartz veinlets occur throughout.
- A late, poor mineralized quartz-eye feldspar porphyry and intermineral porphyry occur from 422.40m to 479.00m. Quartz-sericite alteration predominates with intermediate argillic overprint. Mineralization includes pyrite, chalcopyrite, molybdenite disseminated and in quartz veins in the intermineral quartz-eye feldspar porphyry.
- In the last 82.60m of the hole from 479.00m to 561,60m a quartz-eye feldspar porphyry (intermineral) with abundant Mo veinlets is logged.
Table 3. Summary of Initial Drill Results for Diamond Drill Hole A22-002. All grades are length-weighted averages of samples within the interval reported.
| Hole | From | To | Interval1 | Description | Cu (total) | Mo | Ag | Cueq* |
| ID | m | m | m | % | ppm | ppm | % | |
| A22-002 | 0.10 | 89.40 | 89.30 | Leached | 0.04 | 48.38 | 0.55 | 0.06 |
| 89.40 | 208.00 | 118.60 | Partially Leached | 0.22 | 67.24 | 2.53 | 0.26 | |
| 208.00 | 422.40 | 214.40 | Oxidized/Mixed/Primary | 0.35 | 113.88 | 3.95 | 0.43 | |
| Includes | 244.00 | 296.00 | 52.00 | Primary | 0.52 | 130.55 | 4.53 | 0.61 |
| 422.40 | 479.00 | 56.60 | Primary (Late Porphyry) | 0.09 | 72.09 | 1.29 | 0.13 | |
| 479.00 | 561.60 | 82.60 | Primary – Mo rich | 0.19 | 349.49 | 1.34 | 0.33 |
Note: *Copper equivalent grades (CuEq) are for comparative purposes only. Calculations are uncut and recovery is assumed to be 100% for the 561.60m as the project is at an early stage of exploration and there is insufficient metallurgical data for estimation of metal recoveries.
*Copper-equivalence is calculated as: CuEq (%) = Cu (%) + [3.55 × Mo (%)] + [0.0095 × Ag (g/t)], utilizing metal prices of Cu – US$3.34/lb, Mo – US$11.86/lb and Ag – US$21.87/oz.
1 Intervals are downhole drilled core lengths. Drilling data to date is insufficient to determine true width of mineralization. Assay values are uncut.
Table 4: A22-002 Diamond drill hole location, depth, orientation and dip.
| Hole | Easting | Northing | Elevation | Length | Azimuth | Dip |
| ID | m | m | Degrees | Degrees | ||
| A22-002 | 190,176 | 8,566,179 | 2885 | 561.6 | 235 | 60 |
Co-ordinates are in WGS84 Zone 19S
Quality Control and Quality Assurance
DLP Resources Peru S.A.C a subsidiary of DLP Resources Inc. supervises drilling and carries out sampling of HTW and NTW core. Logging and sampling are completed at a secured Company facility situated on the project site. Sample intervals are nominally 1.5 to 2m in length. Drill core is cut in half using a rotary diamond blade saw and samples are sealed on site before transportation to the ALS Peru S.A.C. sample preparation facility in Arequipa by Company vehicles and staff. Prepared samples are sent to Lima by ALS Peru S.A.C. for analysis. ALS Peru S.A.C. is an independent laboratory. Samples are analyzed for 48 elements using a four-acid digestion and ICP-MS analysis (ME-MS61). In addition, sequential copper analyses are done and reports, soluble copper using sulphuric acid leach, soluble copper in cyanide leach, residual copper and total copper. ALS meets all requirements of International Standards ISO/IEC 17025:2005 and ISO 9001:2015 for analytical procedures.
DLP Resources independently monitors quality control and quality assurance (“QA/QC”) through a program that includes the insertion of blind certified reference materials (standards), blanks and pulp duplicate samples. The company is not aware of any drilling, sampling, recovery or other factors that could materially affect the accuracy or reliability of the data reported to 145.80m in A22-001. From 145.80m to 172.90m in A22-001 core recovery is estimated to be 78% of the total sampled interval and data maybe considered to be “incomplete” and “not representative” for this interval.
Aurora Project
Aurora Project as an advanced stage porphyry copper-molybdenum exploration project in the Province of Calca, SE Peru (Figure 1). The Aurora Project was previously permitted for drilling in 2015 but was never executed. Thirteen historical drill holes, drilled in 2001 and 2005 totaling 3,900m were drilled over an area of approximately 1000m by 800m, cut significant intervals of copper and molybdenum mineralization. From logging of the only three remaining holes DDA-01, DDA-3A and DDA-3 and data now available, it appears that only three of the thirteen holes tested the enriched copper zone and only one hole drilled deep enough to test the primary copper and molybdenum zone (see DLP Resources Inc. news release of May 18, 2021)
Salient historic drill hole data of the Aurora Project are:
-
190m @ 0.57% Cu, 0.008% Mo in DDA-1 with a high-grade intercept of 20m @ 1.01% Cu related to a supergene enrichment zone of secondary chalcocite;
-
142m @ 0.5% Cu, 0.004% Mo in DDA-3;
-
71.7m @ 0.7% Cu, 0.007% Mo in DDA-3A (see historical Focus Ventures Ltd. news release July 11, 2012); and
-
One of the historical holes ABC-6 drilled on the edge of the system intersected 64m @ 0.49% Cu and 0.087ppm Mo (Figure 2)
A review of the historical drilling indicates that the majority of the thirteen holes were drilled in the leached and partially leached zones of the porphyry system. Ten of the thirteen holes never fully tested the oxide and secondary enrichment zone and/or the primary copper zone at depth encountered in DDA-01. Copper-molybdenum mineralization is hosted by quartz-feldspar porphyries intruded into slates-hornfels and pelitic sandstones belonging to the Ordovician (439 – 463 ma) Sandia Formation.
Figure 2. Aurora Project – Simplified geology showing historic drilling and A22-001, A22-002 and A22-003 location
To view an enhanced version of Figure 2, please visit:
Figure 4: Aurora porphyry copper-molybdenum project – Drill core mineralization from A22-002
To view an enhanced version of Figure 4, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/6456/146707_5d97ae92e4fda87c_004full.jpg
To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/146707
Fintech
Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 4, 2025: Maseera, Adva, Plaid, Navi

In today’s ever-evolving fintech landscape, innovation is not merely a buzzword—it is the lifeblood of a dynamic industry that continuously reshapes global finance. This edition of Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief examines the latest pivotal developments that are driving change and fostering new opportunities across financial technology sectors. From strategic acquisitions and regulatory shifts in the buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) sphere to significant funding rounds and data-driven market analyses, the fintech narrative is bursting with energy and potential. In this op-ed-style briefing, we explore how companies like Maseera, Adva, Plaid, and Navi are not only navigating but actively defining the contours of the future of finance.
Our coverage today is rooted in a blend of hard news and informed analysis, as we delve into critical developments reported by renowned sources across the fintech spectrum. Each segment of this article has been meticulously curated and analyzed to provide you with a clear perspective on where the industry stands and where it might be headed. As you read on, you’ll discover insights into strategic expansions, regulatory reforms, and investment trends that are set to shape the fintech environment in the months to come.
Breaking News: Maseera’s Strategic Acquisition of Adva in Egypt
In a significant move aimed at bolstering its regional presence, Maseera’s recent acquisition of Adva marks a major milestone in the expansion of fintech services in Egypt. The acquisition, reported by Tech African News (Source: Tech African News), is poised to redefine how digital financial solutions are deployed in emerging markets.
A New Chapter in Fintech Expansion
Maseera, a recognized name in the fintech arena, has long been at the forefront of digital transformation in finance. With this acquisition, the company not only secures a stronger foothold in Egypt’s burgeoning market but also signals its intent to broaden its portfolio of fintech solutions. The deal is expected to unlock new synergies between Maseera’s technology-driven approach and Adva’s established customer base and operational expertise.
The significance of this acquisition cannot be overstated. In emerging markets, where traditional banking infrastructures often lag behind technological advances, strategic partnerships and acquisitions like this one enable companies to leapfrog legacy systems. By integrating Adva’s services into its own ecosystem, Maseera is poised to offer a seamless, more efficient financial experience to millions of users who are eager for modern digital banking solutions.
Market Impact and Strategic Implications
From an investor’s perspective, the acquisition highlights the potential for exponential growth within the fintech sector, particularly in regions that are ripe for digital disruption. The move is expected to enhance Maseera’s competitive edge, enabling it to offer a broader suite of financial services that cater to both consumer and business needs. Moreover, this deal exemplifies the increasing trend of cross-border investments and strategic consolidations that are redefining the competitive landscape in fintech.
Financial analysts suggest that such strategic moves are critical in a sector where speed and innovation dictate market success. With regulatory frameworks in many emerging economies still in their nascent stages, the agility of fintech firms like Maseera provides them with a unique advantage. The integration of Adva’s operational prowess is likely to streamline processes and introduce innovative products that could significantly disrupt traditional banking paradigms.
Broader Economic and Social Implications
Beyond the immediate business implications, Maseera’s acquisition of Adva holds broader economic significance. As digital financial services become increasingly accessible, they play a pivotal role in driving financial inclusion. For a country like Egypt, which has a significant portion of its population still underbanked, the introduction of advanced fintech solutions can be transformative. It is anticipated that this move will not only boost economic growth but also foster greater transparency and efficiency in financial transactions, ultimately empowering individuals and businesses alike.
Navigating Regulatory Waters: The Future of BNPL in Asia
Regulatory oversight continues to be a critical component in the evolution of fintech, particularly in emerging sectors like BNPL. An insightful piece from Fintech News Singapore (Source: Fintech News Singapore) examines the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for BNPL services in Asia.
The Rise of BNPL and Its Regulatory Challenges
BNPL has rapidly gained traction as a convenient payment method, particularly among younger consumers who favor flexibility over traditional credit lines. However, this rapid adoption has not come without its share of regulatory scrutiny. Policymakers in Asia are increasingly aware of the potential risks associated with BNPL, such as over-indebtedness and lack of consumer protection. As such, regulators are now tasked with striking a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring robust consumer safeguards.
The report emphasizes that the road ahead for BNPL regulation in Asia is complex. Authorities must navigate a landscape that is marked by diverse economic conditions and varying levels of regulatory maturity across different countries. The challenge lies in developing a framework that is both flexible enough to accommodate innovative business models and stringent enough to prevent systemic risks.
Impact on Fintech Companies and Consumers
For fintech companies operating in the BNPL space, the evolving regulatory environment represents both a challenge and an opportunity. On one hand, stricter regulations could potentially slow down the rapid expansion of BNPL services. On the other, a clear regulatory framework could help legitimize the sector, attract more institutional investors, and build greater consumer trust.
From an op-ed perspective, it is crucial to recognize that the proactive steps taken by regulators may ultimately serve to strengthen the fintech ecosystem. Clear guidelines can spur innovation by providing a stable operating environment, thereby reducing uncertainties that often deter investment. Additionally, enhanced consumer protection measures are likely to encourage more widespread adoption, as users gain confidence in the reliability and fairness of BNPL services.
Strategic Recommendations for Industry Players
Industry stakeholders are advised to engage proactively with regulators, contributing their insights to shape a balanced framework that supports both growth and consumer welfare. Fintech companies should invest in robust risk management systems and develop innovative compliance solutions to stay ahead of regulatory changes. Moreover, collaboration with financial institutions and technology partners will be crucial in navigating this evolving landscape successfully.
Plaid’s Robust Funding: Catalyzing Innovation in Digital Finance
In a display of strong market confidence, fintech firm Plaid recently secured a significant round of funding, a development that was detailed by Retail Banker International (Source: Retail Banker International). This funding milestone is not just a financial boost—it is a validation of Plaid’s strategic vision and its critical role in powering digital financial solutions.
The Funding Milestone and Its Significance
Plaid’s successful funding round reflects the broader trend of increased investment in fintech innovations that are transforming the financial services industry. The capital infusion is set to accelerate the company’s development of cutting-edge solutions, enabling it to expand its product offerings and enhance its technological infrastructure. For Plaid, this means a faster rollout of new features that will further streamline the integration of financial data into consumer and business applications.
Investors have shown considerable confidence in Plaid’s ability to navigate a competitive market by continually innovating and adapting to emerging trends. The funding round is indicative of the growing recognition that fintech platforms like Plaid are not merely technology providers, but pivotal enablers of financial inclusion and efficiency. The company’s focus on developing secure, scalable, and user-friendly products aligns perfectly with the evolving needs of modern financial consumers.
Strategic Implications for the Fintech Ecosystem
Plaid’s robust funding serves as a bellwether for the fintech industry, underscoring the importance of investment in technological innovation. With the influx of capital, Plaid is well-positioned to leverage emerging opportunities in areas such as open banking, digital identity verification, and data analytics. This strategic move is likely to have a ripple effect across the fintech ecosystem, inspiring other companies to accelerate their own innovation efforts.
From a broader perspective, the funding success of Plaid highlights the critical role that data integration plays in the digital finance landscape. In an era where data is a key asset, platforms that can seamlessly connect disparate financial systems and provide real-time insights will undoubtedly emerge as leaders in the industry. The funding round is a testament to the value that investors place on companies capable of delivering innovative, data-driven solutions that address the complex needs of today’s financial landscape.
Investor and Consumer Perspectives
For investors, Plaid’s funding round represents a compelling opportunity to capitalize on the rapid growth of digital finance. The company’s strategic vision and its ability to consistently deliver innovative products have positioned it as a standout performer in a crowded market. Meanwhile, consumers stand to benefit from enhanced digital banking experiences that are more secure, efficient, and tailored to their needs.
In this op-ed analysis, it is worth noting that the infusion of capital into fintech firms like Plaid is a harbinger of a more interconnected and data-driven financial future. As these companies continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, they are not only driving market growth but also setting the stage for a new era of financial empowerment.
Q1 Data Analysis: Unveiling Market Trends in Fintech
Data analytics remains one of the most powerful tools in the fintech arsenal. An in-depth analysis of Q1 data, as reported by Sifted (Source: Sifted), provides invaluable insights into the trends that are shaping the fintech landscape. This data-driven approach is critical for understanding market dynamics, forecasting future trends, and making informed strategic decisions.
Key Insights from Q1 Data
The Q1 analysis reveals several noteworthy trends that are influencing the direction of the fintech industry. Among the most significant findings is the rapid pace of digital adoption, particularly in the realm of mobile banking and digital payments. Consumers are increasingly relying on fintech solutions for everyday financial transactions, driven by the convenience and security that these platforms offer.
Furthermore, the data underscores the importance of personalized financial services. As fintech companies harness the power of big data and machine learning, they are better equipped to tailor their offerings to meet the specific needs of individual consumers. This trend towards personalization is not only enhancing customer satisfaction but also driving customer loyalty, as users increasingly expect financial services that are both innovative and user-centric.
Implications for Fintech Companies
For fintech companies, the insights gleaned from Q1 data are invaluable. They highlight the areas where consumer demand is strongest and where investments in technology can yield the highest returns. Companies that can effectively leverage data to anticipate consumer needs and streamline their operations will undoubtedly gain a competitive advantage in the market.
From an op-ed perspective, this data analysis serves as a call to action for fintech leaders. In a rapidly evolving landscape, the ability to harness data and derive actionable insights is a key differentiator. As fintech firms continue to refine their strategies based on data-driven insights, we can expect to see even more innovative products and services that are tailored to the evolving needs of a digital-savvy consumer base.
Broader Market Implications
The Q1 data analysis also provides a broader perspective on the overall health of the fintech industry. It suggests that, despite occasional market fluctuations, the long-term trajectory of digital finance remains robust. The continuous growth in user adoption, coupled with increased investments in technology and innovation, paints a promising picture for the future of fintech.
Moreover, the insights from this analysis have significant implications for policymakers and regulators. As the fintech ecosystem expands, it is crucial for regulatory frameworks to evolve in tandem, ensuring that they support innovation while safeguarding consumer interests. This delicate balance between innovation and regulation is a recurring theme in the fintech narrative, and the Q1 data analysis underscores its importance in shaping a resilient and forward-looking industry.
The Role of Regulators: Insights from Navi’s Perspective
In a candid commentary on the role of regulatory bodies, Navi’s founder, Sachin Bansal, recently shared his perspective on how regulators serve as pivotal stakeholders for fintech companies. This insight was featured on TradingView (Source: TradingView), where Bansal emphasized that “for a fintech, the regulator is its most important stakeholder.”
Understanding the Regulatory Mandate
Bansal’s remarks underscore the complex interplay between innovation and regulation. While fintech companies are celebrated for their disruptive potential and technological prowess, they also operate within a framework that requires strict adherence to regulatory standards. The delicate balance between pushing technological boundaries and complying with regulatory mandates is a recurring challenge for fintech firms.
From an analytical standpoint, Bansal’s perspective invites us to rethink the conventional narrative around regulation. Rather than viewing regulatory oversight as a hindrance to innovation, it can be seen as a necessary partner in ensuring that fintech growth is sustainable, secure, and ultimately beneficial to consumers. Regulatory bodies provide a critical check on potential excesses and help maintain market stability, thereby laying the groundwork for long-term industry success.
Strategic Benefits of Regulatory Collaboration
For fintech companies, forging a collaborative relationship with regulators is not just advisable—it is imperative. Companies that proactively engage with regulatory bodies are better positioned to influence policy development, secure favorable regulatory conditions, and ultimately, drive innovation in a responsible manner. Navi’s emphasis on the regulator as a key stakeholder highlights the need for fintech firms to view regulatory engagement as an integral part of their strategic planning.
In our opinion, the ability to navigate regulatory frameworks effectively is one of the most significant challenges facing fintech companies today. However, those that manage to do so can turn regulatory constraints into competitive advantages by building trust with consumers, enhancing operational resilience, and paving the way for sustained growth.
Looking Ahead: Regulatory Trends and Industry Evolution
As the fintech industry matures, we can expect to see continued evolution in regulatory approaches. Emerging technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and biometric authentication are prompting regulators to rethink traditional frameworks and develop innovative solutions that address the unique challenges posed by digital finance. This dynamic regulatory environment is both a challenge and an opportunity—a duality that industry leaders must navigate with agility and foresight.
Navi’s insights serve as a timely reminder that successful fintech companies must be as adept at regulatory navigation as they are at technological innovation. The future of fintech depends on a collaborative effort between innovators and regulators to create an ecosystem that is secure, transparent, and conducive to sustained growth.
Synthesis and Strategic Outlook: Fintech in the Global Arena
As we synthesize the insights from today’s top fintech stories, several common themes emerge. Innovation, strategic expansion, regulatory engagement, and data-driven decision-making are not isolated trends—they are interwoven elements that collectively define the modern fintech landscape. In our view, the interplay between these factors is shaping a future where digital financial services become increasingly sophisticated, accessible, and integral to everyday life.
Consolidation and Expansion in Emerging Markets
Maseera’s acquisition of Adva is a prime example of how strategic consolidations are driving fintech growth in emerging markets. By combining forces, companies can accelerate innovation, expand their reach, and deliver more comprehensive financial services to underserved populations. This model of strategic expansion is likely to be replicated in other regions, signaling a broader trend toward consolidation that will reshape competitive dynamics in global fintech.
The Dual Edge of Regulatory Oversight
Regulation in fintech is a double-edged sword. While the imposition of regulatory frameworks can sometimes slow down innovation, clear and forward-thinking regulatory policies are essential for ensuring long-term market stability and consumer protection. As evidenced by the discussions surrounding BNPL services in Asia and Navi’s regulatory insights, the future success of fintech hinges on finding a harmonious balance between fostering innovation and maintaining robust oversight.
The Power of Data-Driven Strategies
Data analytics is emerging as a cornerstone of fintech strategy. The insights derived from Q1 data analysis not only validate current trends but also provide a roadmap for future innovation. Companies that can harness the power of data to optimize their products, enhance user experiences, and streamline operations will lead the way in the next phase of digital finance evolution.
Investment and Capital Flow
Plaid’s recent funding round is a testament to the unwavering investor confidence in fintech innovation. Capital investments in fintech are accelerating the development of new technologies, driving competitive dynamics, and ultimately delivering better financial services to consumers worldwide. This influx of funding is instrumental in pushing the boundaries of what is possible in digital finance.
Analyzing the Broader Implications for the Fintech Ecosystem
As fintech continues to disrupt traditional financial systems, it is important to contextualize these developments within the broader economic, technological, and social landscape.
Economic Empowerment and Financial Inclusion
At its core, fintech is about democratizing access to financial services. Strategic moves like Maseera’s acquisition and Plaid’s funding highlight the potential for digital platforms to bridge gaps in financial inclusion, particularly in regions where conventional banking services have historically fallen short. By providing innovative solutions that are both accessible and user-friendly, fintech companies are empowering individuals and businesses to participate more fully in the digital economy.
Technological Disruption and Consumer Behavior
The rapid pace of technological innovation in fintech is reshaping consumer expectations. As users become accustomed to the seamless, on-demand services offered by digital platforms, traditional banks are being forced to adapt or risk obsolescence. The trends discussed in today’s briefing, from BNPL regulation to data analytics, underscore a broader shift toward consumer-centric financial services that prioritize efficiency, transparency, and personalization.
The Role of Strategic Leadership
In an industry marked by rapid change and intense competition, visionary leadership is essential. Companies that can anticipate market trends, navigate regulatory complexities, and drive technological innovation will emerge as the leaders of tomorrow. The examples discussed in today’s briefing—whether it’s Maseera’s bold acquisition strategy or Plaid’s ability to secure significant funding—serve as powerful case studies in strategic leadership within the fintech sector.
Global Collaboration and Cross-Border Innovation
The fintech landscape is inherently global, and today’s developments reflect the interconnected nature of digital finance. Cross-border partnerships and investments are becoming the norm, as companies seek to leverage international expertise and expand their reach. This global perspective is crucial for understanding how local innovations can have far-reaching impacts, influencing market dynamics and regulatory practices worldwide.
In-Depth Commentary: Navigating the Fintech Revolution
As we move further into 2025, the fintech revolution is gathering unprecedented momentum. The stories we have explored today are not isolated incidents but rather interconnected threads in a larger tapestry of digital transformation.
The Convergence of Technology and Finance
At the heart of the fintech revolution is the convergence of advanced technologies—such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and big data—with traditional financial services. This convergence is creating new business models that challenge the status quo and offer consumers unprecedented levels of convenience and security. The recent developments we have covered illustrate this phenomenon vividly. Whether it is through strategic acquisitions, innovative funding strategies, or data-driven insights, fintech companies are reimagining the future of finance with each passing day.
A Call to Innovate and Collaborate
For industry insiders, the message is clear: innovation must be paired with collaboration. Fintech companies that work closely with regulators, technology partners, and even competitors are better positioned to drive sustainable growth. This collaborative spirit is not just a strategic imperative—it is the only viable path forward in a landscape that is as dynamic as it is competitive.
Reflecting on the Journey So Far
Looking back at the evolution of fintech over the past few years, one cannot help but marvel at the speed and scale of change. The rapid digital transformation witnessed across global markets is a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation. However, as we celebrate these advancements, it is equally important to remain vigilant about the challenges that lie ahead, particularly in areas related to cybersecurity, consumer protection, and regulatory compliance.
Balancing Optimism with Prudence
In our opinion, the future of fintech is both bright and complex. While the opportunities are immense, so too are the challenges. Navigating this landscape requires a balanced approach—one that is marked by optimism, but also by a realistic appraisal of the risks and obstacles. As fintech continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, it is incumbent upon industry leaders to ensure that innovation does not come at the expense of security or consumer trust.
The Imperative of Continuous Learning
One of the most compelling lessons from today’s developments is the importance of continuous learning and adaptation. The fintech sector is characterized by rapid change, and what worked yesterday may not necessarily be effective tomorrow. As new technologies emerge and consumer behaviors evolve, staying informed and agile is the key to long-term success. This op-ed-style analysis is intended not only to inform but also to inspire a proactive approach to learning and adaptation within the fintech community.
Conclusion: The Future of Fintech and the Road Ahead
In conclusion, today’s briefing has provided a comprehensive look at some of the most important developments in the fintech industry. From Maseera’s bold acquisition of Adva in Egypt and the evolving regulatory landscape for BNPL in Asia to Plaid’s significant funding round and the illuminating Q1 data analysis, each story underscores the dynamic and multifaceted nature of digital finance today.
Key Takeaways
-
Strategic Expansion: Maseera’s acquisition of Adva is a powerful example of how strategic consolidation can accelerate market penetration in emerging economies, fostering financial inclusion and innovation.
-
Regulatory Evolution: The ongoing discussions around BNPL regulation in Asia highlight the need for a balanced approach that supports innovation while protecting consumers. Regulatory bodies are emerging as key partners in the fintech ecosystem.
-
Investment and Innovation: Plaid’s successful funding round is a clear signal that the market has strong confidence in the fintech revolution. Continued investments in digital finance are expected to drive further technological advancements and market growth.
-
Data-Driven Insights: The Q1 data analysis provides valuable insights into consumer trends and market dynamics, underscoring the importance of leveraging data to drive strategic decision-making in fintech.
-
The Role of Regulators: Navi’s emphasis on regulators as vital stakeholders reinforces the need for fintech companies to work closely with regulatory bodies to ensure sustainable, secure growth.
The Broader Vision
As we look ahead, it is evident that the fintech revolution is far from reaching its zenith. The convergence of technology, strategic investments, regulatory evolution, and data-driven insights is setting the stage for a future where digital financial services become increasingly integral to everyday life. Companies like Maseera, Plaid, and innovators like Navi are leading the charge, paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and dynamic financial ecosystem.
A Call to Action
For industry leaders, investors, and policymakers, today’s developments offer both inspiration and a roadmap for the future. The challenges are significant, but so too are the opportunities. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and remaining steadfast in the pursuit of excellence, the fintech community can drive meaningful change that benefits not only the industry but society at large.
In this fast-paced era of digital transformation, staying ahead of the curve is essential. As we continue to witness rapid advancements and market shifts, the need for continuous learning, agile adaptation, and strategic foresight has never been more critical. The future of fintech is bright, but it will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders to navigate the complex, ever-changing landscape.
Final Thoughts
In wrapping up this comprehensive briefing, it is worth reiterating that the stories and trends discussed today are not isolated—they are part of a broader narrative of digital transformation. The fintech industry stands at the intersection of technology, finance, and innovation, and it is this convergence that promises to unlock unprecedented opportunities in the years to come. As we embrace this future, let us remain committed to the principles of innovation, collaboration, and responsible growth.
Thank you for joining us on this deep dive into the latest fintech developments. We look forward to bringing you more insightful analyses and op-ed-driven commentary as the fintech landscape continues to evolve.
The post Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 4, 2025: Maseera, Adva, Plaid, Navi appeared first on News, Events, Advertising Options.
Fintech
Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 3, 2025 | Plaid, Circle, Finvolution, Fintech Grace

The fintech sector continues to transform at an astonishing pace. Today’s briefing delves into the latest developments shaping the industry—from record-setting funding rounds and strategic IPO preparations to regulatory interventions and groundbreaking international dialogues. As the world of digital finance expands, industry players are not just reacting to market dynamics; they are actively shaping the future of financial technology. This op-ed-style analysis provides a comprehensive look at key developments, exploring their implications and offering insights that go beyond the headlines.
In this in-depth analysis, we cover:
-
Plaid’s Multi-Million Dollar Funding Milestone: An exploration of how one of the leading players in the API space has secured a staggering funding round and what that means for its growth and the broader fintech ecosystem. (Source: CNBC)
-
Circle’s IPO Preparations: A detailed discussion on Circle’s decision to file its registration statement for a U.S.-based IPO and how this move might signal a new era of public market opportunities for digital finance innovators. (Source: Fintech Futures)
-
Regulatory Shake-Up in Connecticut: An examination of the recent mandate requiring a fintech company to repay investors after allegations of fraud, highlighting the increasing scrutiny and the need for robust compliance in an industry that is rapidly evolving. (Source: American Banker)
-
Finvolution’s Globalization Talks: An analysis of Finvolution’s engagement with international bodies such as the United Nations and Pakistani officials, underscoring the global ambition of fintech players and the potential for regulatory harmonization. (Source: PR Newswire)
-
The Rise of Fintech Grace: Insights into the early-stage investment landscape with a focus on Fintech Grace, a company that is positioning itself as a leader in the next wave of fintech innovation. (Source: WWD)
Throughout this article, I will offer a blend of factual reportage and opinion-driven commentary, providing context to help you understand the trends and forces at work in the fintech industry today. Let’s dive into the details of each story and unpack their significance.
The Expanding Fintech Landscape: An Overview
In an industry characterized by rapid innovation and constant change, the fintech sector has evolved into one of the most dynamic and closely watched arenas in the global financial system. As traditional financial institutions face stiff competition from nimble startups, the sector has become a breeding ground for innovation, disruption, and new forms of collaboration. From digital banking to blockchain-based solutions, fintech is not just transforming financial transactions but also reimagining how we interact with money.
Recent months have witnessed several landmark events that underscore the resilience and ambition of fintech companies. Amid a challenging global economic backdrop, companies are raising record amounts of capital, preparing for public listings, and engaging in dialogues that span borders and regulatory frameworks. This diversity of activity reflects the multifaceted nature of fintech—a field that encompasses everything from payment processing and lending platforms to wealth management and cryptocurrency exchanges.
The significance of these developments extends far beyond the balance sheets of individual companies. They represent a broader shift in how financial services are conceived, delivered, and regulated. As consumers demand more seamless and secure digital experiences, fintech firms are not only filling gaps left by traditional banks but also setting new benchmarks for innovation, transparency, and customer engagement.
Market Trends and Key Drivers
Several key trends are driving the fintech revolution today:
-
Increased Capital Injections: Record-breaking funding rounds, like Plaid’s recent success, highlight investors’ confidence in fintech. These capital injections are fueling research, development, and expansion into new markets.
-
Regulatory Scrutiny: With growth comes risk, and regulators are paying closer attention to fintech companies to ensure compliance with financial laws and protect investors. The case in Connecticut serves as a cautionary tale.
-
IPO Movements: As companies like Circle gear up for public offerings, the traditional lines between private innovation and public accountability are blurring. This shift is bringing new challenges and opportunities.
-
Global Expansion: Fintech is no longer confined to local or regional markets. Companies like Finvolution are engaging with global organizations, signaling a trend toward international cooperation and standardization.
-
Emergence of New Players: Early-stage ventures such as Fintech Grace are capturing attention with innovative solutions that could redefine customer experiences and operational efficiencies.
These trends are reshaping the financial landscape, prompting industry insiders to rethink their strategies, operational models, and long-term visions. In the following sections, we examine these developments in greater detail.
Plaid’s Record-Breaking Funding Round: A Catalyst for Growth
One of the standout stories in today’s fintech news is the extraordinary funding round secured by Plaid. Raising an impressive $575 million at a valuation of $6 billion, Plaid has once again demonstrated its pivotal role in connecting financial data to innovative digital applications.
The Details Behind the Funding
Plaid, renowned for its ability to facilitate seamless connections between banks and apps, has long been a crucial enabler in the fintech ecosystem. This new infusion of capital is expected to not only bolster its technological capabilities but also extend its market reach. Investors are betting on Plaid’s robust business model and its critical role in the digital finance infrastructure, ensuring that the company remains at the forefront of fintech innovation.
The funding round has set a high bar, underscoring the growing appetite among venture capitalists for fintech solutions that streamline financial interactions in an increasingly digital world. The impressive valuation reflects both the company’s current achievements and its potential for future growth.
Industry Implications
The implications of Plaid’s successful funding round are far-reaching:
-
Accelerated Innovation: With new resources at its disposal, Plaid can accelerate the development of its products, enhancing functionalities that are crucial for both businesses and consumers.
-
Increased Market Penetration: The capital will enable Plaid to expand its services into new markets, both domestically and internationally, further solidifying its position as an indispensable partner in the digital finance ecosystem.
-
Competitive Benchmark: For competitors and newcomers alike, Plaid’s valuation serves as a benchmark, driving innovation and encouraging other companies to push the envelope in their offerings.
While some skeptics might point to the risks inherent in high valuations, the current market sentiment remains overwhelmingly positive. Investors are clearly optimistic about the future of financial technology and the role that companies like Plaid will play in shaping that future.
(Source: CNBC)
Circle’s Bold Move Towards an IPO
Another major highlight in the fintech news cycle is Circle’s decision to file a registration statement for an IPO in the United States. This move represents a significant milestone for a company that has consistently been at the forefront of digital asset innovation.
The Strategic Rationale
Circle’s registration for an IPO is emblematic of the broader trend among fintech companies seeking to transition from private to public markets. The decision to go public is not made lightly; it reflects the company’s confidence in its growth trajectory and its ability to meet the stringent requirements of public market scrutiny. The move is expected to provide Circle with a more robust platform for scaling its operations, diversifying its revenue streams, and enhancing its brand visibility.
This strategic step also comes at a time when the cryptocurrency and digital asset markets are maturing. With increasing institutional acceptance and a growing regulatory framework, Circle’s IPO could serve as a bellwether for other fintech companies contemplating similar transitions. The public market listing will also offer retail investors a direct opportunity to participate in the growth story of a company that has been a key innovator in the digital finance space.
Broader Market Impact
Circle’s IPO registration has several broader implications:
-
Market Validation: An IPO is a powerful signal of market maturity and investor confidence. Circle’s move can validate the fintech model for other companies in the space, paving the way for a wave of similar listings.
-
Enhanced Transparency: Public companies are subject to rigorous disclosure and regulatory standards, which can enhance transparency and accountability—an increasingly important factor for investors in the fintech space.
-
Innovation Catalyst: The infusion of public capital can drive further innovation within Circle, allowing the company to invest in new technologies and expand its service offerings.
Critics, however, caution that the transition to public markets will also bring challenges, including heightened scrutiny, the need for robust corporate governance, and the pressure of meeting quarterly expectations. Nevertheless, the overall sentiment remains optimistic, with many analysts predicting that Circle’s IPO could herald a new era of growth for the digital asset industry.
(Source: Fintech Futures)
Regulatory Developments: Connecticut Orders Fintech Repayment
While the market continues to celebrate new funding rounds and IPO preparations, regulatory developments remind us that the fintech industry is not immune to scrutiny. A recent decision in Connecticut has forced a fintech firm to repay $843,000 to defrauded investors, underscoring the importance of compliance and ethical business practices.
Unpacking the Incident
The case in Connecticut highlights the challenges that fintech companies face in maintaining transparency and safeguarding investor interests. The repayment order was issued following an investigation into practices that misled investors, emphasizing that even in a sector defined by innovation, there must be strict adherence to regulatory standards.
This incident serves as a stark reminder of the potential pitfalls in the fintech space, where rapid growth and a relentless drive to innovate can sometimes lead to oversights. Regulatory bodies are increasingly vigilant, ensuring that companies do not compromise on the principles of fairness and accountability.
Lessons for the Industry
The Connecticut case offers several critical lessons for fintech firms:
-
Rigorous Compliance: As fintech companies expand their operations, they must invest in robust compliance frameworks to prevent fraudulent activities and protect investors.
-
Transparency as a Cornerstone: Trust is the foundation of the fintech industry. Ensuring transparency in all dealings not only safeguards investor interests but also builds long-term credibility.
-
Proactive Regulatory Engagement: Companies that proactively engage with regulators and adopt best practices in corporate governance are better positioned to navigate the complex regulatory landscape.
-
Risk Management: In a fast-moving market, establishing strong risk management protocols is essential. This includes regular audits, independent oversight, and a culture of accountability.
For investors and industry stakeholders, the Connecticut decision is both a cautionary tale and a call to action. It reinforces the need for vigilance and robust governance frameworks, particularly as fintech companies continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
(Source: American Banker)
Finvolution’s Globalization Talks: A Step Toward International Collaboration
In a move that signals the global ambitions of fintech firms, Finvolution has entered into discussions with the United Nations and Pakistani officials to explore opportunities for fintech globalization. This groundbreaking initiative is aimed at harmonizing financial technologies across borders, setting the stage for increased cooperation and innovation on a global scale.
The Essence of Globalization in Fintech
Finvolution’s talks represent a significant step in recognizing that fintech is not confined by geographical boundaries. In an increasingly interconnected world, the need for standardized practices, regulatory harmonization, and cross-border collaboration is more pressing than ever. By engaging with global institutions like the United Nations, Finvolution is positioning itself as a leader in driving international dialogue on fintech best practices.
These discussions are expected to cover a broad range of topics, including cybersecurity, digital identity, regulatory standards, and sustainable finance. The aim is to create an environment where fintech innovation can thrive while ensuring that the global financial system remains secure and inclusive.
Strategic Implications for the Industry
The implications of Finvolution’s international engagement are profound:
-
Regulatory Harmonization: One of the most significant challenges facing the fintech industry is the patchwork of regulatory regimes across different jurisdictions. Global talks can pave the way for more uniform standards that benefit both companies and consumers.
-
Cross-Border Investment: As regulatory barriers decrease, there is potential for increased cross-border investment and collaboration, opening up new avenues for growth and innovation.
-
Enhanced Security Protocols: International dialogue can lead to the development of more robust cybersecurity measures, ensuring that fintech systems are resilient against global threats.
-
Promotion of Inclusion: Global standards can help ensure that fintech innovations are accessible to a broader population, supporting financial inclusion initiatives worldwide.
The initiative taken by Finvolution highlights the importance of viewing fintech not just as a local or national phenomenon but as a global movement with the potential to redefine how financial services are delivered around the world.
(Source: PR Newswire)
Fintech Grace: Pioneering the Next Wave of Innovation
The final piece in today’s briefing centers on Fintech Grace—a rising star in the fintech arena that has recently attracted significant seed investment. While still in the early stages of its journey, Fintech Grace embodies the innovative spirit that is driving the sector forward.
The Investment and Its Implications
Seed investments are often the lifeblood of innovation, and Fintech Grace is no exception. The recent seed investment signals a strong vote of confidence from early-stage investors who see great potential in the company’s business model and technology. As Fintech Grace positions itself to capitalize on emerging market trends, this investment will enable the company to accelerate its product development, expand its team, and explore new market opportunities.
This development is particularly noteworthy because it highlights a broader trend: while mega funding rounds for established players like Plaid dominate headlines, the seed-stage landscape remains fertile ground for groundbreaking ideas and disruptive technologies. Investors are increasingly aware that the next big breakthrough in digital finance might well come from a small, agile startup capable of pivoting quickly to address unmet needs.
Broader Industry Impact
The rise of Fintech Grace is significant for several reasons:
-
Innovation Pipeline: Emerging startups like Fintech Grace are the testing grounds for new ideas that could revolutionize digital finance. Their successes can spur further innovation across the industry.
-
Diverse Investment Opportunities: The infusion of capital into seed-stage ventures broadens the spectrum of investment opportunities, fostering a more diverse and resilient fintech ecosystem.
-
Market Disruption: Startups with innovative solutions have the potential to disrupt traditional models, driving incumbents to innovate or risk obsolescence.
-
Inspirational Leadership: The story of Fintech Grace serves as an inspiration for other entrepreneurs who dare to challenge the status quo in a rapidly evolving market.
The excitement surrounding Fintech Grace underscores the dynamic nature of the fintech space, where innovation can emerge at any stage of a company’s lifecycle. It is a testament to the industry’s ongoing evolution and the unyielding drive to redefine how we interact with financial systems.
(Source: WWD)
Expert Analysis: Connecting the Dots in Today’s Fintech Landscape
Each of these stories tells a part of the larger narrative that is unfolding in the fintech sector. Together, they offer a window into the multifaceted nature of digital finance—a space where rapid innovation, regulatory challenges, and global ambitions converge to create an ever-changing landscape.
Innovation and Investment: A Symbiotic Relationship
The infusion of capital into established players like Plaid, coupled with the bold steps of companies like Circle, highlights the robust relationship between innovation and investment. When investors place their bets on fintech companies, they are not merely funding a business model; they are endorsing a vision of a more interconnected, efficient, and customer-centric financial future. However, as the stakes rise, so does the need for accountability and sound governance, as evidenced by the regulatory actions in Connecticut.
The dynamic interplay between private investment and public market activity is another aspect worth noting. As fintech companies transition from private startups to publicly listed entities, they bring with them a level of transparency and accountability that can drive broader market confidence. This transition is crucial for the sustainability of the industry, ensuring that the high-flying ambitions of today are matched by robust structures for tomorrow.
The Role of Regulation in Sustaining Growth
While the rapid pace of innovation is a source of optimism, regulatory oversight remains a critical component of the fintech ecosystem. The case in Connecticut is a clear reminder that financial innovation must go hand in hand with consumer protection and ethical business practices. As fintech companies continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, regulators are tasked with striking the delicate balance between fostering innovation and safeguarding public trust.
In a landscape marked by rapid change, proactive regulatory engagement is more important than ever. Companies that adopt a forward-looking approach to compliance are likely to fare better in the long run, building resilient business models that can withstand both market turbulence and evolving regulatory frameworks.
Globalization: Expanding the Horizons of Fintech
The engagement of Finvolution in globalization talks represents a paradigm shift for the fintech industry. No longer confined by national borders, fintech companies are now looking to create networks of collaboration that span continents. This global perspective not only expands market opportunities but also encourages the harmonization of standards—a development that could ultimately lead to a more stable and secure global financial system.
By integrating diverse perspectives and regulatory practices, the fintech industry can better navigate the complexities of a digital economy that is increasingly interconnected. This shift toward globalization is a clear indicator that the future of finance lies in international cooperation, where best practices are shared and innovations are scaled across different markets.
The Road Ahead: Trends and Predictions
As we look ahead, several trends are likely to shape the fintech landscape:
-
Sustained Investment: Despite economic headwinds, investment in fintech is expected to remain robust. Companies that continue to innovate and adapt to changing market dynamics are poised to attract significant capital.
-
Evolving Regulatory Frameworks: As fintech solutions become more embedded in everyday life, regulators will likely introduce new frameworks to ensure consumer protection and systemic stability. This evolution will require companies to remain agile and proactive in their compliance efforts.
-
Expansion into New Markets: With globalization in full swing, fintech companies are set to explore untapped markets, leveraging technology to offer financial services to a broader audience. This trend is likely to drive financial inclusion and spur economic growth in emerging regions.
-
Focus on Security and Transparency: In an era marked by cybersecurity threats and data privacy concerns, fintech firms will need to invest heavily in secure technologies and transparent practices to maintain consumer trust.
-
Integration of Emerging Technologies: From artificial intelligence and blockchain to biometric authentication, the integration of emerging technologies will continue to drive the evolution of fintech, creating new opportunities and challenges alike.
The interplay of these factors will define the future trajectory of the fintech sector, creating an environment that is as challenging as it is full of potential.
Concluding Thoughts: Navigating the Future of Fintech
Today’s fintech landscape is a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation. With significant capital injections, bold strategic moves, and an increasing emphasis on regulatory compliance and international collaboration, the industry is poised for transformative change. The stories we’ve explored today—from Plaid’s record-breaking funding round and Circle’s IPO ambitions to the regulatory intervention in Connecticut and Finvolution’s globalization talks—each contribute a vital piece to the intricate puzzle of modern finance.
As an industry observer, it is clear that the fintech sector is not merely a collection of isolated incidents or fleeting trends. Instead, it represents a profound shift in the way we understand, interact with, and manage financial systems. The decisions made by companies today will have long-lasting effects on consumer behavior, regulatory policies, and the overall stability of the financial ecosystem.
Looking ahead, fintech leaders must balance ambition with prudence. The drive to innovate must be tempered with a commitment to ethical practices and regulatory compliance. Investors, too, have a role to play, as their support can fuel the next wave of transformative technologies—if only they remain vigilant about the risks inherent in such rapid growth.
For the consumer, the promise of fintech is one of convenience, efficiency, and empowerment. As companies like Plaid, Circle, Finvolution, and Fintech Grace continue to push the boundaries, they are not just building products; they are crafting experiences that could redefine the relationship between individuals and their finances. This evolution, however, requires constant dialogue between industry players, regulators, and consumers—a dialogue that ensures innovation is both responsible and inclusive.
In conclusion, today’s briefing is a call to action for everyone involved in the fintech ecosystem. The momentum is undeniable, the challenges are real, and the potential is limitless. As we navigate these transformative times, let us remain committed to a future where technology and finance merge to create a system that is innovative, secure, and accessible to all.
In-Depth Perspectives: Expert Opinions and Market Insights
In the dynamic world of fintech, opinions matter as much as hard data. Industry experts are increasingly vocal about the need for innovation that is grounded in sound business practices and robust regulatory oversight. Here, we delve into some of the expert perspectives that are shaping today’s discourse:
Balancing Disruption with Responsibility
Many experts believe that while fintech companies must remain agile and innovative, there is no substitute for a strong ethical foundation. The recent regulatory action in Connecticut serves as a stark reminder that market disruption must not come at the expense of investor trust and consumer protection. Thought leaders argue that the fintech industry should adopt a model of “responsible disruption,” where innovation is pursued with an unwavering commitment to transparency and accountability.
This perspective is particularly relevant in light of the rapid capital inflows witnessed in the sector. As investors continue to pour money into fintech startups and scale-ups, the pressure to perform can sometimes overshadow the need for robust risk management. By focusing on responsible innovation, companies can mitigate these risks while still capturing the immense opportunities that lie ahead.
The Global Fintech Ecosystem: Challenges and Opportunities
Internationalization is not just a buzzword; it is an inevitable outcome of the digital age. Experts contend that the path to a truly global fintech ecosystem involves reconciling diverse regulatory frameworks, technological standards, and cultural differences. Finvolution’s recent engagement with global organizations is a positive step in this direction. It demonstrates that fintech is not merely a collection of local innovations but a globally integrated movement that can drive financial inclusion and economic growth on a massive scale.
The road to globalization is, however, fraught with challenges. Harmonizing regulatory standards and ensuring data security across borders require sustained dialogue and cooperation. Industry leaders emphasize that collaboration—rather than competition—will be the key to unlocking the full potential of a global fintech ecosystem.
Looking Ahead: Trends That Will Define the Next Decade
Several trends are poised to shape the future of fintech:
-
Technological Integration: The blending of traditional financial services with cutting-edge technology will create hybrid models that are more efficient, secure, and customer-centric.
-
Evolving Consumer Expectations: As digital natives become the dominant consumer demographic, the demand for personalized, seamless financial services will only grow.
-
Sustainability and Social Impact: Beyond profit, fintech companies are increasingly expected to contribute to social and environmental goals. Sustainable finance initiatives and impact investing are becoming integral parts of many firms’ strategies.
-
The Rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi): With blockchain technology maturing, decentralized financial services are set to challenge traditional banking models, offering new ways for consumers to access financial products and services.
By embracing these trends, fintech companies can position themselves not only as industry leaders but as pioneers of a new financial paradigm that is both inclusive and forward-thinking.
Final Reflections: The Intersection of Innovation, Regulation, and Global Vision
As we wrap up today’s industry brief, it is important to reflect on the interconnectivity of the developments we’ve discussed. Innovation in fintech is not a standalone phenomenon—it is deeply intertwined with regulatory frameworks, global ambitions, and evolving consumer needs. The successful funding of Plaid, the IPO preparations at Circle, the regulatory intervention in Connecticut, the international talks spearheaded by Finvolution, and the seed investment in Fintech Grace all point to a sector in the midst of profound transformation.
This convergence of innovation, regulation, and globalization presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the rapid pace of technological advancement promises to revolutionize financial services, making them more accessible and efficient than ever before. On the other hand, the need for robust oversight and ethical governance cannot be understated. Fintech companies must navigate these dual imperatives if they are to sustain long-term growth and deliver value to both investors and consumers.
As an industry observer and analyst, I see today’s news as part of a broader narrative—a narrative that speaks to the potential of fintech to redefine how we live, work, and interact with money. The future of finance is being written today, with each decision, investment, and regulatory action contributing to a legacy that will shape the industry for years to come.
The landscape ahead is both exciting and uncertain. Yet, what remains clear is that fintech will continue to be a force of transformation, driven by the twin engines of innovation and collaboration. For investors, entrepreneurs, regulators, and consumers alike, staying informed and engaged is essential. The stories we’ve explored today are more than just headlines—they are the building blocks of a future where financial services are not only more advanced but also more equitable and secure.
In closing, let this daily briefing serve as both an update and an invitation—a call to delve deeper into the forces shaping our financial future and to actively participate in a dialogue that is as dynamic as the industry itself.
A Glimpse Into Tomorrow’s Fintech World
Looking to the horizon, it is evident that the fintech sector will continue to evolve in unexpected ways. Technological breakthroughs, evolving regulatory landscapes, and the drive for global integration will all play a role in defining the next chapter of digital finance. As we consider the road ahead, several key areas warrant special attention:
The Convergence of Technology and Finance
The fusion of technology and finance is accelerating, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics. These technologies are not only enhancing operational efficiencies but also enabling entirely new business models that can disrupt traditional financial services. In the coming years, we can expect to see a greater integration of these technologies, leading to innovations that redefine risk assessment, customer engagement, and financial management.
Consumer Empowerment Through Digital Innovation
At the heart of fintech’s promise is the empowerment of consumers. As digital solutions become more sophisticated, they offer unprecedented levels of personalization and convenience. From mobile banking apps that provide real-time insights to automated investment platforms that democratize access to financial markets, the modern consumer is more informed and empowered than ever before. This trend is likely to accelerate, with companies continuously seeking to tailor their offerings to meet the evolving demands of a tech-savvy population.
Regulatory Evolution in a Digital Age
The regulatory environment for fintech is set to undergo significant changes as lawmakers and industry experts work to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring systemic stability. Future regulations are expected to be more adaptive, leveraging technology to monitor compliance in real time while providing clear guidelines that encourage responsible innovation. This proactive regulatory stance will be essential in building a resilient financial system that can adapt to rapid technological change.
Global Integration and Collaborative Innovation
The international dimension of fintech will become increasingly important as companies seek to expand their horizons beyond domestic markets. Collaborative initiatives like Finvolution’s global talks represent a positive step towards creating a harmonized regulatory and operational framework across borders. This global integration will facilitate the free flow of capital, ideas, and technology, further driving innovation and economic growth on a worldwide scale.
The Role of Investment in Shaping the Future
Investment remains a critical driver of fintech innovation. The continued interest from venture capitalists, institutional investors, and even retail investors will provide the necessary fuel for startups and established companies alike to experiment, innovate, and scale. As funding strategies evolve and new financial instruments emerge, the fintech ecosystem will become even more dynamic, with investment decisions playing a key role in determining which innovations ultimately succeed in the marketplace.
A Comprehensive Recap of Today’s Headlines
To summarize today’s key developments in the fintech world:
-
Plaid’s Funding Triumph: With a remarkable $575 million raised at a $6 billion valuation, Plaid’s achievement underscores the importance of robust financial infrastructure in driving digital innovation. Investors continue to back the company’s vision, signaling strong market confidence in its ability to lead the fintech revolution.
(Source: CNBC) -
Circle’s IPO Preparations: Circle’s filing of a registration statement for a U.S.-based IPO marks a pivotal moment in its evolution, reflecting the growing maturity of digital asset markets and the company’s readiness to embrace public market discipline. This move could pave the way for other fintech innovators to follow suit, bridging the gap between private innovation and public accountability.
(Source: Fintech Futures) -
Connecticut’s Regulatory Intervention: The decision to mandate a fintech company to repay $843,000 to defrauded investors in Connecticut serves as a critical reminder of the need for transparency, ethical practices, and rigorous compliance in an industry marked by rapid innovation and high stakes.
(Source: American Banker) -
Finvolution’s Globalization Initiative: By engaging in discussions with the United Nations and Pakistani officials, Finvolution is charting a course for international collaboration, highlighting the potential for harmonized regulatory frameworks and global financial integration that could benefit the industry as a whole.
(Source: PR Newswire) -
The Emergence of Fintech Grace: The recent seed investment in Fintech Grace signals strong early-stage interest in innovative fintech solutions, emphasizing that groundbreaking ideas can originate from startups poised to disrupt traditional models and drive the future of digital finance.
(Source: WWD)
Each of these stories, while distinct in its focus, contributes to the overarching narrative of a fintech industry that is bold, innovative, and increasingly global in its outlook. They are not isolated incidents but interconnected developments that together signal a transformative era in financial technology.
Final Words: Embracing a New Era in Fintech
In reflecting on today’s developments, it becomes clear that the fintech industry is at a crossroads—where innovation meets regulation, where local successes inspire global ambitions, and where financial services are being reimagined for a digital future. This dynamic interplay of investment, strategy, and oversight is reshaping the industry, presenting both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges.
As fintech companies continue to evolve, they must balance their drive for innovation with a commitment to ethical practices and consumer protection. Investors, regulators, and industry leaders alike must collaborate to build a framework that not only nurtures creativity but also safeguards the integrity of financial systems worldwide.
The future of fintech is bright, yet it demands vigilance, adaptability, and a forward-thinking approach. By staying informed, engaging in constructive dialogue, and embracing the inevitable changes that lie ahead, all stakeholders in the ecosystem can contribute to building a financial landscape that is inclusive, secure, and innovative.
Thank you for joining me on this detailed exploration of today’s fintech news. As we navigate these transformative times together, let us keep our focus on what matters most: driving progress in a way that benefits everyone.
The post Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 3, 2025 | Plaid, Circle, Finvolution, Fintech Grace appeared first on News, Events, Advertising Options.
Fintech
Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 2, 2025 | Featuring Citi, Insigneo, Luma Financial Technologies, Weefin, Tirana Bank, Backbase

In today’s fast-paced financial technology landscape, industry players are constantly reinventing their approaches and challenging traditional norms. As fintech continues to disrupt the financial services sector, we bring you a detailed daily briefing that not only summarizes the latest developments but also offers an op-ed-style analysis of where the market is heading. This in-depth article explores five significant news pieces shaping the industry, each accompanied by our insights, expert commentary, and a comprehensive breakdown of emerging trends. Join us as we delve into transformative leadership moves, promising startup comebacks, strategic partnerships, capital infusions for ESG data management, and cutting-edge core banking technology collaborations.
A Shifting Leadership Landscape: Citi’s Transformation and Its Ripple Effects
One of the most noteworthy stories today comes from the corridors of global finance. A key executive from Citi’s transformation team has made a surprising move by departing for a new challenge in the problematic payments fintech sector. This shift is more than just a personnel change—it signals deeper structural transformations within major financial institutions as they recalibrate their strategies in the digital age.
Breaking Down the Departure
The departure of Citi’s transformation managing director is not merely a human resources update; it’s a sign of the times. In an era where digital transformation is at the forefront, the ability to navigate regulatory changes, adopt innovative payment technologies, and meet evolving consumer expectations is paramount. The executive’s move highlights the growing demand for agile leadership capable of steering large organizations through complex transitions.
Source: eFinancialCareers
Implications for the Industry
This leadership change has several implications for the broader fintech ecosystem:
-
Leadership Realignment: Large institutions like Citi are reevaluating their talent strategies as digital and payments technologies evolve. When top-level executives jump ship, it often catalyzes a reexamination of company priorities and may accelerate internal reforms.
-
Focus on Problematic Payments: The fact that the new role is centered on problematic payments is a reminder of the persistent challenges in the payments space. Issues such as transaction errors, fraud prevention, and cross-border complexities continue to require innovative solutions.
-
Market Opportunity for Fintech Startups: Such high-profile moves create opportunities for fintech startups and mid-sized companies to attract experienced professionals. The infusion of leadership talent from established banks could help these companies accelerate product development and market penetration.
Strategic Analysis
From an op-ed perspective, this development reflects a broader trend: the gradual erosion of the traditional banking model. As banks struggle to keep pace with technological change, seasoned leaders are increasingly drawn to roles where innovation isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity. The move can be seen as a microcosm of the fintech revolution itself, where adaptability and forward-thinking leadership become the currency of success.
While Citi has long been a pillar of financial stability, this recent change may prompt the institution to double down on its digital transformation initiatives. The departure suggests that even the largest banks cannot rest on their laurels; they must constantly evolve to survive in an era defined by rapid technological disruption and fierce competition from nimble fintech startups.
The Fintech Comeback: VC Startups on the Rise
In another compelling piece of news, PitchBook’s recent article highlights the resurgence of fintech startups fueled by robust venture capital interest. After a period of market volatility and investor caution, there is now a renewed optimism that fintech innovation will not only recover but also redefine financial services for the modern era.
A Renewed Investment Wave
The narrative of a fintech comeback is gaining traction as venture capital firms begin pouring funds into promising startups. This influx of capital is critical to sustaining innovation in an industry that thrives on disruption. Investors are drawn by the potential for fintech solutions to democratize financial services, enhance operational efficiency, and provide more personalized experiences for consumers.
Source: PitchBook
Key Trends in Fintech Investment
Several trends underscore this revival:
-
Digital Transformation: Investors are increasingly interested in companies that leverage digital technologies to streamline traditional financial processes. The focus is on scalable platforms that offer mobile-first solutions, cloud-based operations, and real-time data analytics.
-
Diversification of Offerings: The fintech landscape is diversifying rapidly. Beyond the conventional payments and lending sectors, there is growing interest in wealth management, insurance tech, regtech, and blockchain-driven solutions.
-
Sustainable and Inclusive Finance: There is a rising tide of investment in fintech companies that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. These startups are not just about profit—they are about driving meaningful change in how financial services are delivered.
The Role of Venture Capital
Venture capitalists have long recognized the disruptive potential of fintech. Today, their renewed commitment signals confidence in the ability of startups to challenge incumbent banks and reshape the competitive dynamics of the financial industry. With more capital at their disposal, these companies are better positioned to scale operations, innovate product lines, and expand into untapped markets.
Opinion and Forecast
From an op-ed standpoint, the fintech comeback represents a significant shift in investor sentiment. It suggests that the market has learned from previous setbacks and is now more attuned to the risks and rewards inherent in fintech ventures. In our view, this resurgence is not merely a cyclical rebound but a fundamental reordering of priorities. As digital-first consumers continue to drive demand for more agile and personalized financial services, fintech startups will be at the forefront of this transformation.
This reinvigoration of venture capital investment underscores the notion that fintech is here to stay. Investors and industry leaders alike must keep an eye on these emerging trends, as they are likely to herald a new era of financial innovation—one characterized by increased competition, enhanced customer experiences, and a more inclusive financial ecosystem.
Strategic Partnerships: Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies Join Forces
In another major development, Insigneo has announced a strategic partnership with Luma Financial Technologies. The collaboration aims to upgrade structured note product capabilities and enhance advisor efficiencies. This alliance is a classic example of how fintech companies are pooling their expertise to create synergies that drive both innovation and operational excellence.
The Rationale Behind the Partnership
The partnership between Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies is grounded in the belief that combining complementary strengths can yield substantial benefits for the market. Structured notes, which are complex financial instruments combining bonds and derivatives, require robust technology to manage their intricacies. By partnering with Luma Financial Technologies, Insigneo is positioned to offer more refined products and improved advisory services.
Source: FF News
Enhancing Structured Note Capabilities
Structured notes have long been a niche yet essential part of the investment landscape. They offer investors tailored exposure to various asset classes and risk profiles. However, their complexity often limits their accessibility. With this partnership, both companies are set to streamline the creation, management, and distribution of these financial products. Key enhancements include:
-
Technology Integration: Leveraging Luma’s advanced technology platform to automate processes, reduce errors, and enhance real-time analytics.
-
Product Customization: Enabling more personalized and flexible structured note products that can be tailored to meet specific investor needs.
-
Operational Efficiency: Improving advisor workflows by providing integrated tools that support client interactions and decision-making processes.
Broader Market Implications
This strategic alliance has significant ramifications for the fintech landscape:
-
Innovation in Financial Products: As the complexity of financial instruments increases, partnerships like this one are critical to making sophisticated products more accessible to a broader audience.
-
Competitive Edge: By enhancing their product offerings, Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies are better positioned to compete with larger, more established financial institutions. This partnership could set a precedent for future collaborations in the fintech space.
-
Client-Centric Solutions: The emphasis on advisor efficiency underscores a shift towards more client-centric approaches. Financial advisors, empowered by innovative technology, can now offer more informed and customized investment strategies.
Analyzing the Partnership from an Opinion Perspective
In our view, this partnership is emblematic of the collaborative spirit that defines today’s fintech ecosystem. Rather than competing in isolation, fintech companies are increasingly recognizing the value of strategic alliances. This trend not only accelerates innovation but also fosters a more resilient financial services environment. With technology playing a central role, such collaborations are poised to redefine market dynamics, making advanced financial products accessible and efficient for a wider range of investors.
The Insigneo-Luma partnership is a bold step forward. It signals a move towards a more integrated financial landscape where technology and traditional expertise converge. As the fintech industry evolves, we expect to see more alliances like this—each contributing to a broader, more inclusive transformation of financial services.
ESG and Data Management: Weefin’s E25M Raise Spurs New Developments
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria have become essential benchmarks in today’s investment decisions, and fintech companies are no exception. In a notable development, Weefin, an ESG data management fintech, has successfully raised €25 million. This funding injection is set to enhance its data management capabilities and drive innovations in ESG reporting and analytics.
The Importance of ESG in Fintech
ESG is no longer just a buzzword; it is a critical component of strategic decision-making across industries. In fintech, the ability to analyze and report on ESG factors is increasingly becoming a competitive differentiator. Investors are looking for companies that not only deliver financial returns but also demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and responsible governance.
Source: Markets Media
Weefin’s Strategic Move
Weefin’s successful raise is a testament to the growing importance of ESG metrics in the financial sector. The company’s focus on data management in this space is particularly timely given the increasing regulatory and consumer demand for transparency. With the new funding, Weefin is positioned to:
-
Enhance Data Analytics: Invest in state-of-the-art technology that improves the accuracy and speed of ESG data processing.
-
Expand Market Reach: Increase its footprint in global markets by offering robust ESG reporting tools that cater to a diverse range of financial institutions.
-
Drive Innovation: Develop new products and services that leverage big data and artificial intelligence to provide actionable ESG insights.
Broader Implications for the Fintech Sector
Weefin’s capital raise has broader implications for the industry:
-
Investor Confidence: The successful funding round signals strong investor confidence in fintech solutions that address ESG challenges. This confidence is likely to spur further investment in companies operating at the intersection of finance and sustainability.
-
Regulatory Alignment: With regulators worldwide emphasizing ESG disclosure, fintech companies that can deliver reliable, high-quality data management solutions will have a distinct advantage.
-
Market Differentiation: In an increasingly crowded market, having robust ESG data management capabilities can serve as a key differentiator, helping companies build trust with clients and stakeholders.
Opinion-Driven Insights
In our analysis, Weefin’s €25 million raise is not just a financial milestone; it is a strategic signal of the future direction of fintech. As sustainability and responsible governance become non-negotiable for investors and regulators alike, companies that invest in advanced ESG data management will be at the forefront of the next wave of financial innovation. We believe that this funding round will catalyze further advancements in ESG analytics, ultimately leading to a more transparent and accountable financial system.
The emphasis on ESG also reflects a broader shift in investor priorities. No longer can companies afford to ignore the environmental and social dimensions of their operations. As fintech firms continue to develop and implement sophisticated ESG tools, they will not only comply with emerging regulations but also drive meaningful change in how financial success is defined.
Advancing Core Banking Technology: Tirana Bank Partners with Backbase
In a further illustration of the relentless pace of innovation in fintech, Tirana Bank has entered into a strategic partnership with Backbase to enhance its engagement banking platform. This collaboration represents a significant leap forward in core banking technology, underscoring the growing importance of digital transformation in the banking sector.
Transforming the Core Banking Experience
The partnership between Tirana Bank and Backbase is focused on creating a more engaging and intuitive banking experience for customers. In today’s digital era, banks are compelled to move beyond traditional transactional models and offer services that are seamless, personalized, and accessible through multiple channels.
Source: Fintech Futures
Key Components of the Partnership
Several elements make this partnership particularly noteworthy:
-
Engagement Banking Platform: The new platform is designed to integrate various customer touchpoints, from mobile apps to online banking portals, ensuring a consistent and engaging user experience.
-
Technology Modernization: Backbase’s advanced technology will enable Tirana Bank to modernize its core banking systems, improving operational efficiency and customer service.
-
Personalization and Data Analytics: By leveraging sophisticated data analytics, the platform will allow for personalized financial advice and product recommendations, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and retention.
-
Agility in Digital Innovation: The collaboration is a strategic move to ensure that Tirana Bank remains competitive in a rapidly evolving financial landscape. The ability to quickly adopt new technologies is essential for meeting the dynamic needs of today’s consumers.
Market Trends and Broader Context
The partnership aligns with several prevailing market trends:
-
Digital-First Banking: Consumers increasingly expect banks to provide digital-first services that are not only efficient but also engaging and user-friendly.
-
Technology-Driven Transformation: As banks face pressure to update legacy systems, partnerships with fintech companies like Backbase are becoming more common, driving significant improvements in service delivery.
-
Enhanced Customer Engagement: The focus on engagement banking reflects the broader industry trend towards a more customer-centric approach, where personalized services and real-time interactions are paramount.
Op-Ed Perspective on the Partnership
From an analytical standpoint, the Tirana Bank and Backbase partnership is a harbinger of the digital revolution sweeping through the banking sector. In our view, this move is not merely about technology adoption—it represents a fundamental rethinking of how banks engage with their customers in the digital age. By investing in a robust engagement platform, Tirana Bank is positioning itself to meet the challenges of tomorrow while enhancing its competitive edge today.
This initiative underscores the critical importance of agility and innovation in financial services. Traditional banks, long seen as slow to adapt, are now embracing the transformative potential of fintech solutions. The collaboration between Tirana Bank and Backbase is a clear indicator that the future of banking will be defined by digital engagement, seamless integration of services, and a relentless focus on customer satisfaction.
Synthesis and Future Outlook
Bringing these diverse news items together, one theme stands out: the relentless pace of change in the fintech landscape. Whether it is leadership realignment at global institutions, a resurgence in venture capital investment, strategic partnerships to drive product innovation, significant capital raises for ESG initiatives, or transformative advancements in core banking technology, the industry is undergoing a profound transformation.
Key Themes Across the Stories
-
Leadership and Talent Mobility: The departure of top executives from established banks like Citi illustrates a broader trend of talent migration toward fintech roles. This movement is accelerating innovation as experienced leaders bring their expertise to emerging sectors.
-
Investment and Innovation: The fintech comeback driven by renewed venture capital investment signals a robust future for startups and established players alike. With more capital in the market, companies are poised to deliver breakthrough products that cater to an increasingly digital and discerning customer base.
-
Strategic Collaborations: Partnerships such as those between Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies, and between Tirana Bank and Backbase, demonstrate how collaboration is essential for overcoming the complexities of modern financial services. These alliances enable companies to pool resources, share expertise, and rapidly innovate.
-
Sustainability and ESG: Weefin’s successful raise is a clear indicator of the growing importance of ESG in fintech. With investors and regulators demanding greater transparency and accountability, companies that can deliver sophisticated ESG solutions will lead the way.
-
Digital Transformation: Across all these stories, the common thread is the imperative to adopt and integrate digital technologies. The transformation of core banking systems, the drive to enhance customer engagement, and the development of agile, scalable platforms all point to a future where technology is the backbone of financial services.
Industry Analysis and Strategic Commentary
In our expert opinion, these developments are more than isolated news items—they are indicative of a broader, systemic transformation within the financial services industry. The rapid evolution of fintech is disrupting established paradigms and challenging long-held assumptions about banking, payments, and financial management. Here are some key insights:
-
The Evolution of Consumer Expectations: Today’s consumers are more tech-savvy and demand seamless, personalized experiences. Financial institutions that fail to innovate risk becoming obsolete in an increasingly competitive market.
-
Collaboration Over Competition: The trend towards strategic partnerships suggests that collaboration is emerging as the preferred strategy for navigating technological disruption. By combining forces, companies can achieve synergies that drive innovation and create value for customers.
-
The Role of Regulation and Compliance: As fintech continues to grow, regulatory frameworks will need to adapt. Companies that proactively address compliance and transparency, particularly in ESG, will have a competitive advantage.
-
The Future of Traditional Banking: Traditional banks are facing unprecedented pressure to modernize. While the departure of top executives may be seen as a negative indicator, it also presents an opportunity for these institutions to reinvent themselves by adopting new technologies and business models.
Looking Ahead
As we look to the future, it is clear that fintech will continue to shape the financial services industry in profound ways. The interplay of technology, investment, and strategic partnerships will drive innovation and redefine customer experiences. Financial institutions must remain agile, continually reassessing their strategies to stay relevant in this dynamic environment.
The current wave of transformation is not without its challenges. Issues such as cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and technological integration will require ongoing attention and investment. However, the potential rewards are immense. For investors, consumers, and financial institutions alike, the ongoing fintech revolution offers the promise of more efficient, transparent, and inclusive financial services.
In conclusion, today’s news stories—from leadership shifts and investment booms to strategic partnerships and technological breakthroughs—offer a glimpse into the future of finance. As the fintech landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to capitalizing on emerging opportunities and navigating potential risks.
Deep Dive: Fintech Trends and the Road Ahead
The Digital Transformation Imperative
The digital transformation of financial services is not merely a trend; it is a fundamental shift in how value is created and delivered. Traditional banking models, which once relied on physical branch networks and legacy systems, are rapidly being replaced by digital-first approaches. This shift is driven by several key factors:
-
Consumer Behavior: With the ubiquity of smartphones and high-speed internet, consumers expect instant, secure, and convenient access to financial services. Digital platforms meet these expectations by offering 24/7 accessibility, seamless transactions, and personalized experiences.
-
Cost Efficiency: Digital solutions reduce operational costs by streamlining processes, automating routine tasks, and eliminating the need for extensive physical infrastructure. This efficiency allows financial institutions to reallocate resources towards innovation and customer service.
-
Data-Driven Insights: Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence enable financial institutions to harness vast amounts of data. This data-driven approach supports better decision-making, risk management, and the creation of personalized financial products.
The Role of Venture Capital in Driving Innovation
Venture capital plays a pivotal role in propelling fintech innovation forward. The renewed wave of investment, as highlighted by PitchBook, signals that investors are confident in the long-term potential of fintech startups. Several factors contribute to this confidence:
-
Scalability of Digital Solutions: Fintech startups often operate on platforms that can rapidly scale to serve millions of users. This scalability is attractive to investors who see the potential for significant returns.
-
Disruptive Business Models: Fintech companies frequently challenge traditional financial paradigms with innovative business models that leverage technology to deliver superior customer experiences.
-
Global Reach: Digital platforms are not confined by geographic boundaries. Startups that offer mobile-first solutions can tap into global markets, creating exponential growth opportunities.
ESG as a Strategic Priority
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations have moved to the forefront of investment strategies. Weefin’s recent funding round is a strong indicator that ESG is not just a regulatory requirement but also a strategic priority for fintech companies. Here’s why ESG matters:
-
Investor Demand: Modern investors are increasingly prioritizing companies that demonstrate strong ESG practices. A solid ESG profile can enhance a company’s reputation and attract long-term capital.
-
Risk Management: Incorporating ESG factors into business operations can mitigate risks related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices.
-
Competitive Advantage: As more financial institutions integrate ESG metrics into their operations, those with robust ESG data management capabilities will stand out in the market.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborative Innovation
The fintech landscape is evolving from a competitive arena into a collaborative ecosystem. Partnerships such as those between Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies, and between Tirana Bank and Backbase, exemplify this trend. The benefits of such collaborations include:
-
Resource Sharing: Combining expertise and resources allows companies to innovate faster and overcome operational challenges.
-
Market Expansion: Partnerships provide access to new markets and customer segments, driving growth and diversification.
-
Enhanced Product Offerings: By pooling their technological capabilities, partnering companies can develop more sophisticated products and services that better meet customer needs.
The Future of Financial Services
Looking ahead, the fintech industry is poised to deliver a host of transformative innovations. Here are some predictions for the future:
-
Increased Personalization: With advancements in data analytics and machine learning, financial services will become increasingly personalized, offering tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of each customer.
-
Greater Integration of AI: Artificial intelligence will play an ever-growing role in risk management, fraud detection, and customer service, making financial operations more efficient and secure.
-
Expansion of Digital Currencies and Blockchain: Digital currencies and blockchain technology are set to revolutionize payment systems, offering faster, more secure, and cost-effective solutions for cross-border transactions.
-
Emergence of New Financial Models: As technology continues to disrupt traditional banking, new financial models—such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and embedded finance—will emerge, challenging conventional norms and creating new avenues for innovation.
Expert Opinions: Voices from Within the Industry
Throughout today’s briefing, it is evident that the fintech sector is characterized by rapid innovation and strategic repositioning. Industry leaders and experts have offered varied insights on these developments, emphasizing the importance of agility, collaboration, and a forward-thinking mindset.
Leadership Transitions and Industry Evolution
The departure of a key Citi executive is emblematic of the broader shifts occurring in financial services. Industry insiders suggest that such transitions are not isolated incidents but part of a larger trend where experienced professionals are seeking opportunities in more dynamic and innovative environments. The migration of leadership talent from traditional banks to fintech firms is expected to accelerate the pace of digital transformation and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Venture Capital’s Renewed Optimism
The resurgence of venture capital investment in fintech is generating considerable excitement. Experts highlight that the increased capital flow is a vote of confidence in the transformative potential of digital financial services. This optimism is backed by tangible improvements in technology, customer engagement, and operational efficiency observed across the industry.
The Growing Importance of ESG
ESG considerations are becoming central to strategic decision-making in fintech. Analysts underscore that companies capable of integrating robust ESG data management systems will not only meet regulatory demands but also capture market share by appealing to socially conscious investors and customers. The funding success of Weefin is viewed as a harbinger of more widespread adoption of ESG principles in the fintech ecosystem.
Collaborative Innovation as the New Norm
Strategic partnerships are increasingly seen as essential for survival in today’s competitive environment. The alliances between Insigneo and Luma Financial Technologies, and between Tirana Bank and Backbase, are perfect examples of how collaboration can lead to mutually beneficial outcomes. These partnerships are expected to set new benchmarks for product innovation and operational excellence in the financial services industry.
In-Depth Analysis: Navigating Uncertainty and Seizing Opportunities
Understanding the Risk Landscape
Despite the immense opportunities presented by digital transformation, the fintech industry is not without its challenges. Cybersecurity threats, regulatory uncertainties, and market volatility are perennial concerns. However, the proactive measures taken by industry leaders—from strategic partnerships to significant capital investments—demonstrate a commitment to mitigating these risks.
-
Cybersecurity: As digital transactions become more prevalent, ensuring the security of sensitive financial data is paramount. Fintech companies are investing heavily in advanced security protocols and encryption technologies to protect against breaches and fraud.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex web of global financial regulations is a constant challenge. Firms that can integrate compliance into their core operations while still innovating are likely to emerge as market leaders.
-
Market Volatility: The fintech sector is inherently dynamic, with rapid shifts in investor sentiment and consumer behavior. Companies must remain agile and adaptable to weather economic fluctuations and capitalize on emerging trends.
Strategic Recommendations for Industry Stakeholders
Based on our analysis, here are several strategic recommendations for fintech companies and investors:
-
Invest in Talent and Leadership: As demonstrated by recent leadership moves, attracting and retaining top talent is critical. Organizations should create environments that foster innovation and support continuous learning.
-
Embrace Digital Transformation: Firms that prioritize digital initiatives and invest in scalable technologies are better positioned to meet modern consumer demands.
-
Foster Strategic Collaborations: Forming alliances with complementary fintech companies can unlock new opportunities and drive innovation faster than working in isolation.
-
Prioritize ESG and Transparency: Integrating robust ESG practices is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative. Companies that can offer transparent, data-driven ESG solutions will gain a competitive edge.
-
Focus on Customer-Centric Solutions: With consumer expectations rapidly evolving, delivering personalized, intuitive, and engaging financial services should be at the forefront of any strategic initiative.
The Broader Societal Impact
The ripple effects of these developments extend beyond the confines of the financial services industry. As fintech companies continue to innovate, they are also reshaping societal expectations around access to finance, transparency, and accountability. This transformation has the potential to democratize financial services, making them more accessible and equitable for people across different socioeconomic backgrounds.
Moreover, as sustainability and responsible governance become integrated into financial models, the impact on broader societal goals—such as reducing carbon footprints and promoting social justice—will be significant. In our view, the successful integration of ESG principles within fintech not only drives business success but also contributes to a more sustainable and inclusive global economy.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Fintech
The fintech landscape is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by transformative leadership changes, renewed venture capital interest, strategic partnerships, and a heightened focus on ESG and digital transformation. Today’s news—from the departure of a key Citi executive and the resurgence of VC-backed fintech startups to the strategic alliances of Insigneo with Luma Financial Technologies and Tirana Bank with Backbase, as well as Weefin’s impressive funding round—paints a vivid picture of an industry in flux.
In our op-ed-style analysis, we have explored the intricate interplay of these factors, highlighting not only the challenges but also the vast opportunities that lie ahead. The future of fintech is being written by companies that dare to innovate, collaborate, and embrace change. For investors, consumers, and industry professionals, the key takeaway is clear: adaptability, strategic foresight, and a commitment to technological excellence will be the hallmarks of success in this brave new world of financial services.
As we continue to witness the evolution of digital banking, payments, and financial management, we remain committed to providing you with insightful commentary and comprehensive analysis. Stay tuned for more updates as we track the pulse of fintech and offer you the daily industry brief that not only informs but also inspires.
The post Fintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 2, 2025 | Featuring Citi, Insigneo, Luma Financial Technologies, Weefin, Tirana Bank, Backbase appeared first on News, Events, Advertising Options.
-

 Fintech5 days ago
Fintech5 days agoFintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – March 29, 2025 Featuring: Charlie Javice, Rabobank, Mollie, Ivy, Barclays, and more
-

 Fintech3 days ago
Fintech3 days agoFintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 2, 2025 | Featuring Citi, Insigneo, Luma Financial Technologies, Weefin, Tirana Bank, Backbase
-

 Fintech4 days ago
Fintech4 days agoFintech Pulse: Your Daily Industry Brief – April 1, 2025 Featuring: Neobanks, Fintech Innovators, Spendr, Financial Finesses, Elga Credit Union, Pocketnest
-

 Fintech PR3 days ago
Fintech PR3 days agoAbeille Assurances Relies on Location Intelligence and Data Enrichment from Precisely to Manage Climate Risks and Enhance Customer Experience
-

 Fintech PR2 days ago
Fintech PR2 days agoKuCoin Surpasses 40 Million Registered Users, Demonstrating Commitment to Compliance and Innovation
-

 Fintech PR2 days ago
Fintech PR2 days agoNewmark’s First Quarter 2025 Financial Results Announcement to be Issued Prior to Market Open on Wednesday, April 30, 2025
-

 Fintech PR1 day ago
Fintech PR1 day agoANDURAND CAPITAL CEASES TO RELY ON ALTERNATIVE MONTHLY REPORTING SYSTEM; URGES SPROTT TO FIX SPROTT COPPER VEHICLE
-

 Fintech PR3 days ago
Fintech PR3 days agoEY upgrades Nightfall, a zero-knowledge roll-up enabling private transactions on the Ethereum blockchain








